
Many people can suffer from pain in their hip or groin for prolonged periods of time before receiving a correct diagnosis. The hip is a ball and socket joint, in which the head of the femur inserts into the acetabulum. Surrounding the acetabular cup is the labrum, which is a fibrocartilaginous tissue that helps to deepen the acetabular socket. It is believed that the labrum can act as a lubricator by helping to prevent direct contact with the cartilage. Hip labral tears are becoming a common hip injury. There are several factors that can contribute to a labral tear, one of which is a Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI).
FAI is caused by abnormalities in the bone structure of the hip joint. There are two types of impingements that can occur: CAM and Pincer . While a person can suffer from only one of the impingements, approximately 86% of patients suffer from both.1 A CAM type impingement occurs when there is an abnormality in the femoral head, compared to a pincer impingement that occurs as a result of an abnormality in the acetabulum.3 Women are at a higher risk of developing a pincer impingement.1 Maximal contact between the acetabular labrum and the anterosuperior femoral head-neck junction occur during internal rotation and flexion of the hip.3 Repetitive movement can cause the labrum to tear. It is also believed that FAI can eventually lead to the onset of osteoarthritis.1, 4 FAI can be either asymptomatic or symptomatic, but if it is symptomatic surgery may be required.
Arthroscopic surgery is performed for those who meet the criteria for hip labral surgery . Arthroscopic hip surgery has seen a tremendous increase in popularity over the last 10 years, with an increase in occurrence of 250% between 2007-2011.5 During surgery, the surgeon will correct any bone abnormalities present and reattach the labrum to the acetabular rim. If one does not have enough labrum, the doctor may use an autograft or cadaver allograft using Iliotibial band (IT band) in order to perform a Labral Reconstruction .
Post-surgical rehabilitation generally takes about 12 weeks and is supervised by a physical therapist. Unlike many surgeries, rehabilitation will begin either the same day as surgery or the next morning. The patient will begin the ride a stationary bike as soon as possible, sometimes the same day depending on the doctor’s protocol. External rotation and abduction of the hip are limited by a hip brace. In addition, anti-rotation bands may be used to help limit tension to the repaired structures. Patients will typically remain non-weight bearing through the first phase of therapy, which can last about 4 to 6 weeks. The first phase of rehabilitation focuses on circumduction and passive motion. Phase two of rehabilitation focuses on early strength exercises, aimed at restoring the hip flexors, hamstrings, quadriceps, glutes and IT band.4 It also encompasses neuromuscular re-education and stabilization exercises for the hips and spine. For patients who will be returning to sports, functional rehabilitation may also begin at this stage. The last phase continues to focus on strength training and sport-specific exercises. Patients can sometimes return to sport as soon as four months after surgery.4
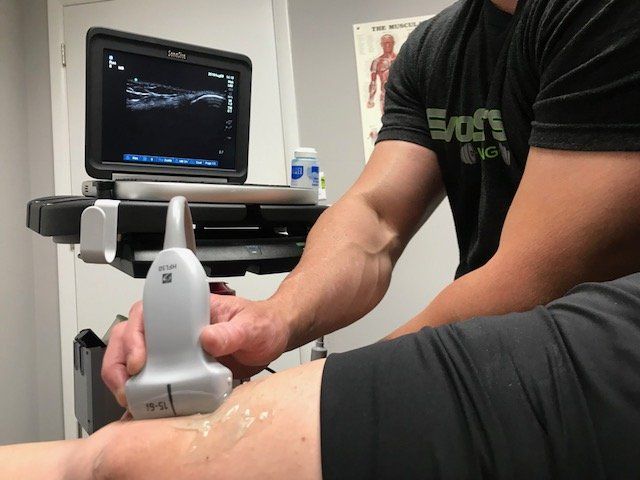
It is important to note that conservative or nonoperative management can be a viable and successful option for patients who may be suffering from symptoms related to FAI or Hip labral pathology. A recent systematic review of research studies looking at nonoperative treatment of FAI demonstrates that there are favorable findings for conservative intervention with hip impingement patients.6 Given the various disorders capable of causing hip pain, it is important that a careful and comprehensive examination of the hip joint and its surrounding structures be completed prior to patients immediately opting for surgical intervention. Physical therapists are wonderful resources to utilize for these examinations and subsequent treatment to address any deficits or biomechanical errors. Physical therapists have the ability to perform and interpret findings of diagnostic ultrasound in order to further evaluate the integrity of the internal hip capsule. This offers patients the opportunity to have a picture of their hip joint without the hassle of setting up an appointment for an MRI and waiting for the results to be given by a radiologist.
In terms of the physical exam, the deficits typically seen with hip impingement cases include poor posterior joint play, increased hip adduction and/or internal rotation during functional activities (running, cycling, jumping, etc.), as well as weak and/or tight surrounding hip/gluteal musculature.7 The development of a precise, individualized physical therapy program to address each patient’s deficits can assist with patients avoiding surgical intervention. Physical therapists will employ various manual therapy techniques and therapeutic exercises/activities that will improve posterior hip joint play, strengthen hip musculature in closed and open chain positions while working in all three planes of movement, and correcting faulty biomechanics/movement patterns in order to reduce the stresses placed on the hip joint and decrease instances of hip impingement.
Hip impingement and hip labral tears are becoming more understood, and more doctors and physical therapists are competent in the differential diagnostic process in recognizing this pathology.
For more information on evaluation and treatment at Evolution Sports , click here .
References:
1) Alradwan, H., Philippon, M.J., Farrokhyar, F., Chu, R., Whelan, D., Bhandari, M., & Ayeni, O.R. (2012). Return to preinjury activity levels after surgical management of famoroacetabular impingement in athletes. Arthroscopy, 28 (10).
6) Wall, P.D. et al (2013). Nonoperative treatment for femoroacetabular impingement: a systematic review of the literature. PM & R, 5 (5), 418-426.
7) Loudon, J.K. & Reiman, M.P. (2014). Conservative management of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) in the long distance runner. Physical Therapy in Sport , 15: 82-90.




Evolution Sports Physiotherapy offers a wide variety of rehabilitation services. Our highly trained team members attend ongoing training to ensure patients like you enjoy the best care possible.
Established in 2008, we work with many insurance companies. However, See us for strength and conditioning, concussion management, and other rehabilitative needs. Read more about our PT centers.
Evolution Sports Physiotherapy
10540 York Road, Suite F-G
Cockeysville, MD 21030
410-628-0520